SAPPHIRE
Sapphire and ruby are members of the corundum family, a group of crystallized aluminum oxides. Both have exactly the same chemical composition and only small amounts of coloring trace elements distinguish between them. Sapphire and ruby both are considered among the most important and valuable gemstones available.
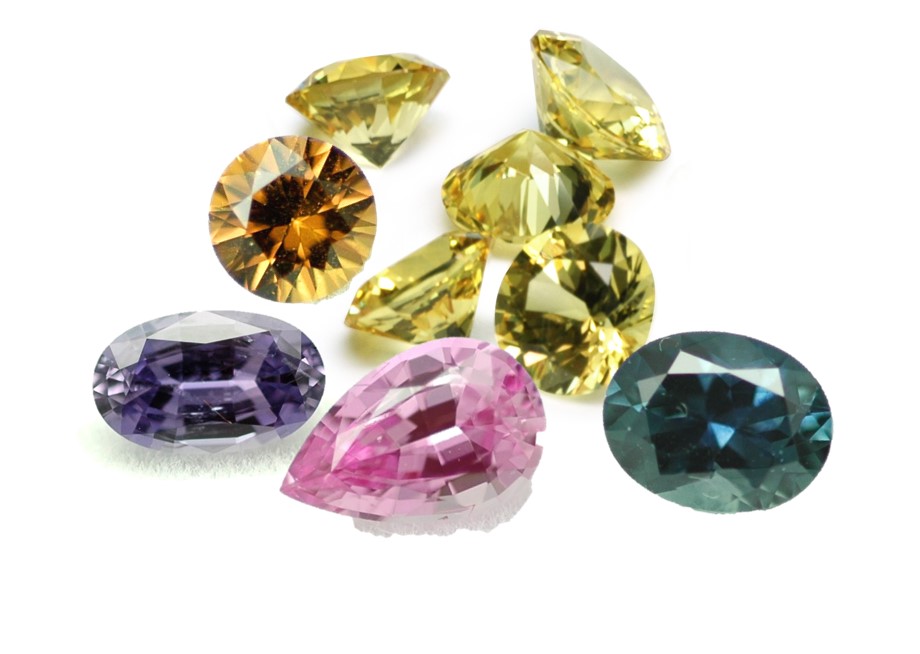
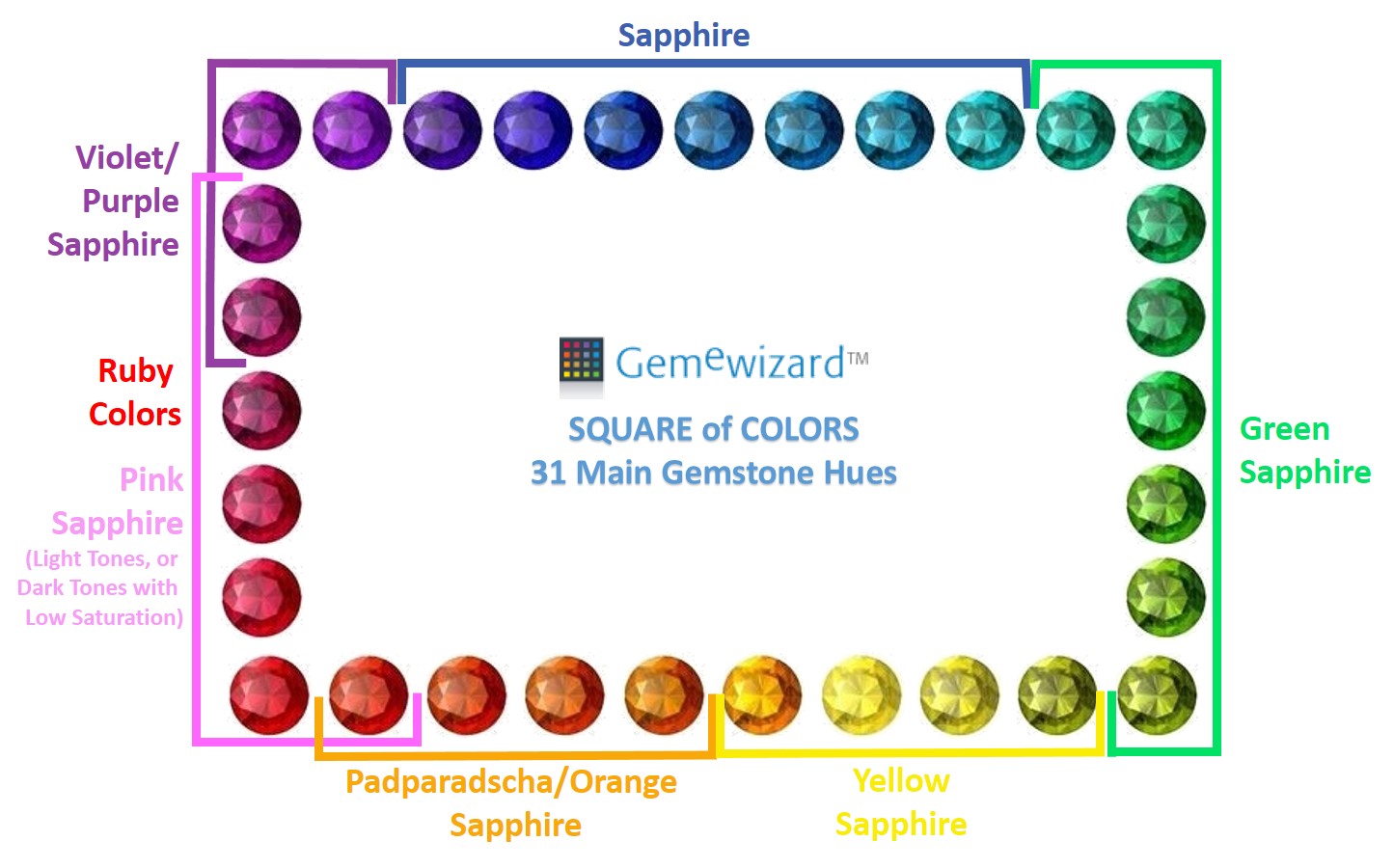
Sapphire appears in all possible colors except red, such as blue, yellow, green, purple, pink and brown. The term Sapphire, when used on its own, refers only to the blue variety of sapphires, which ranges from very strongly greenish Blue to Blue to bluish Violet, while sapphires in all other colors (also known as ‘Fancy sapphires’) occupy the rest of the entire spectrum and are named together with their associated color prefix, such as ‘orange sapphire’, ‘pink sapphire’, ‘green sapphire’ etc. In the purple to red region, which is also associated with Ruby colors, a gem with low saturation of purple-red will be defined as ‘Pink Sapphire’ or ‘Purple Sapphire’ (according to the tone). Color is the most important characteristic that determines the sapphire's value.
The name Sapphire is derived from the Persian word Safir.
LEGEND AND LORE
Sapphire is the birthstone for the month of September and the gemstone representing the fifth and 45th wedding anniversaries.
It was believed that sapphires could influence spirits and reveal the secrets of oracles. They were deemed to attract wealth, bring harmony between lovers, make peace between enemies and protect the wearer from envy and infidelity. They were also thought to strengthen the well-being and overall health of the owner, clear the mind and skin, cure fevers, colds, eye diseases and ulcers and were used as an antidote to poison. Sapphire is a long-time symbol and guardian of purity and it represents truth, sincerity, and consistency. Sapphire is mentioned in the Bible as one of the gemstones on the High Priest's breastplate.

SAPPHIRE COLORS
Sapphire appears in all possible colors except red, such as blue, yellow, green, purple, pink, brown and colorless. The various colors are a result of different trace elements in the crystal structure.
Sapphirel is allochromatic, meaning its colors are derived from impurities in its crystal structure and when the stone is pure, it is colorless.
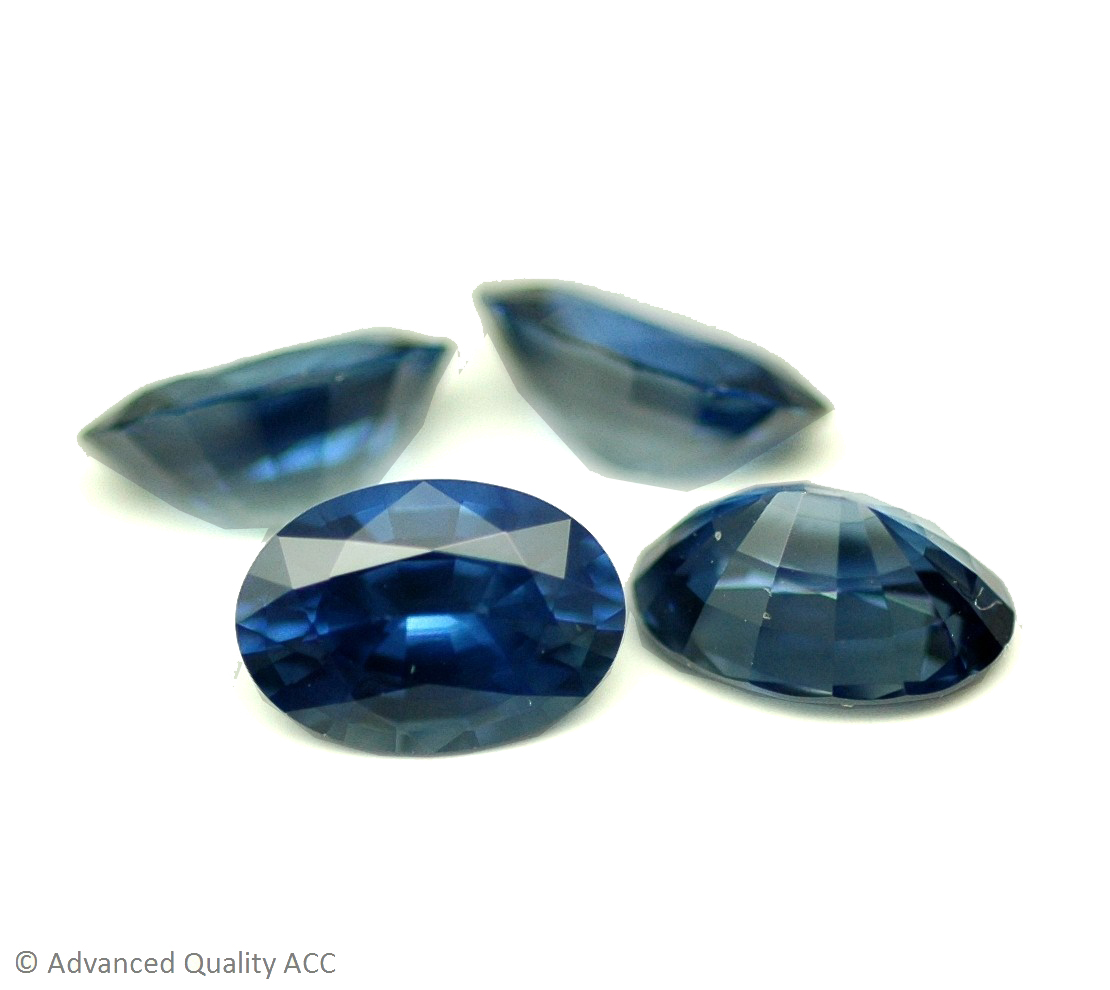
SAPPHIRE (BLUE) 
The term Sapphire, when used on its own, refers only to the blue variety of sapphires, which ranges from very strongly greenish Blue to Blue to bluish Violet. Among the blues, two colors are considered to be the most sought after – ‘Royal Blue’, the most desired and most valued shade within the trade, and ‘Cornflower Blue’, resembling the color of the famous flower.
Sapphires from Myanmar (Burma) and Kashmir are considered the most valuable.
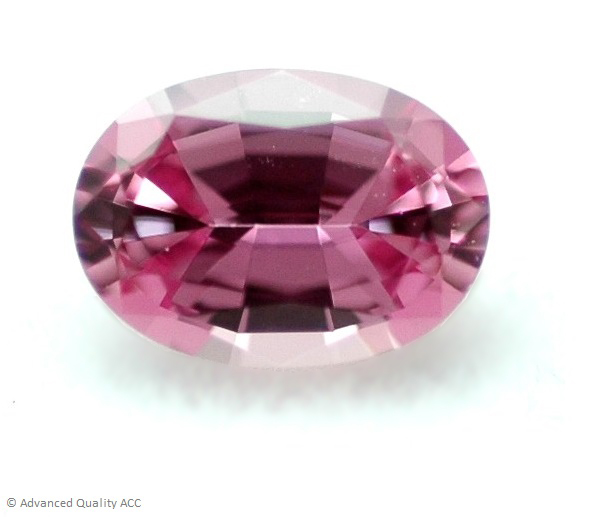
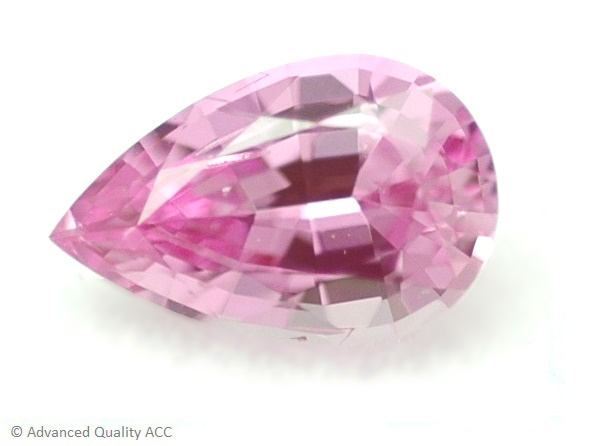
PINK SAPPHIRE 
Pink sapphire is typically found in colors of a bright, delicate pink to a pink with a slight tinge of violet. It is considered to be the highest valued fancy colored sapphire. The border between pink sapphire and ruby is vague and differs between different markets around the world.
PURPLE & VIOLET SAPPHIRE 
Purple sapphire colors range from violetish Purple, which is designated a Violet Sapphire, to Red-Purple, which is identified as Purple Sapphire.
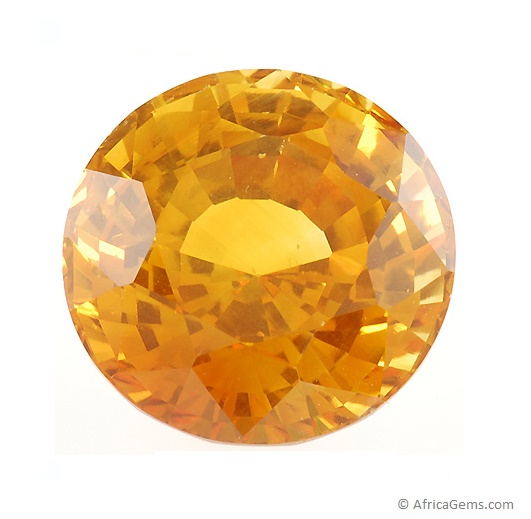
YELLOW SAPPHIRE 
Yellow sapphire ranges in color from pale to canary yellow, gold, honey, and brownish yellow and is found in quite large quantities. The lighter and brighter colors are the most common, whereas golden yellow gemstones of high quality are very rare and command high prices. Yellow sapphires with another noticeable secondary hue, such as green, grey or brown or orange tint, are more common.
ORANGE SAPPHIRE 
Pure orange sapphires are very rare and very popular among collectors. Most of the orange sapphires display a yellow, red or brown tint.
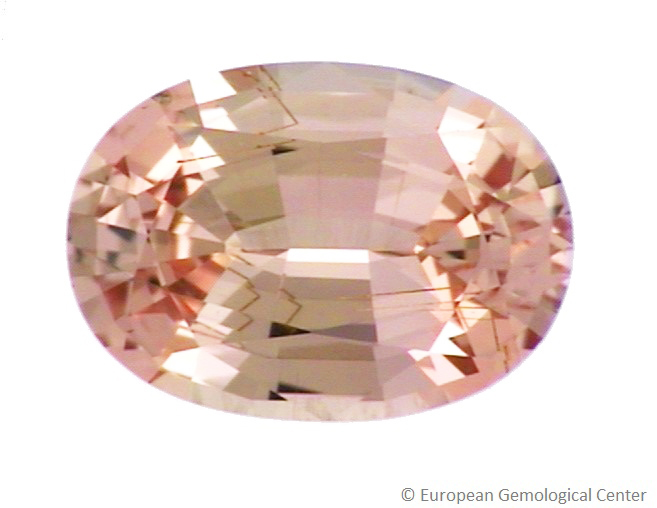
PADPARADSCHA SAPPHIRE 
Light Pink-Orange colored sapphires from Sri-Lanka are called ‘Padparadscha sapphire’, named after the padparadscha lotus flower. This gemstone is very beautiful and rare, and currently is in great demand by collectors. There are African sapphires which have an orange-red color reminiscent of the valuable padparadscha sapphires of Sri Lanka, albeit possessing a more brownish tint. These gems are termed African padparadscha.
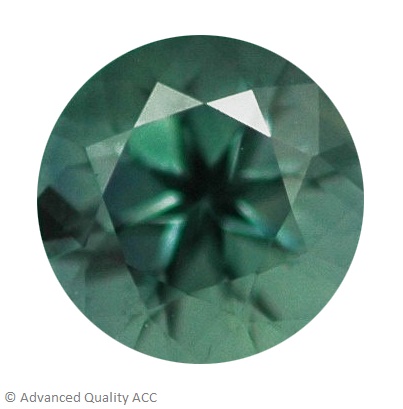
GREEN SAPPHIRE 
Green sapphire colors range from Yellow-Green to Blue-Green, where the majority displays bluish Green colors with a metallic greyish tint.
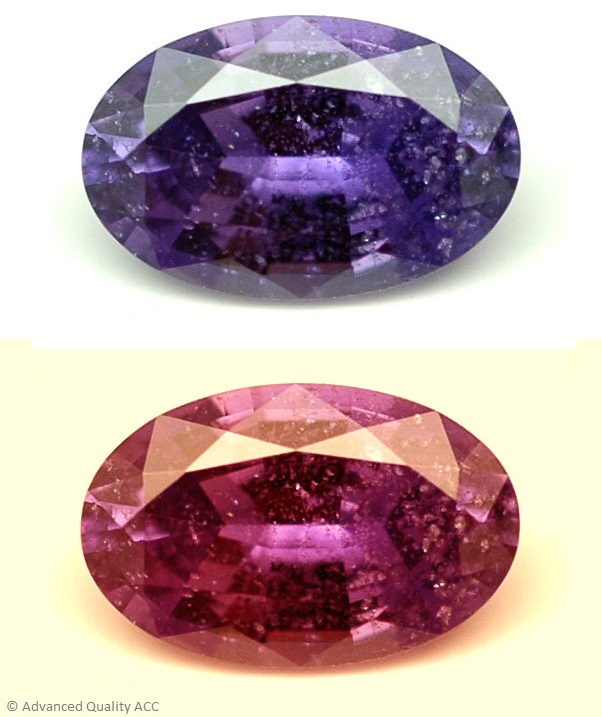
COLOR CHANGE & STAR SAPPHIRE 

Sapphires displaying special phenomena are very rare and are mostly treasured by collectors. Color-change sapphires display much stronger than the usual color shifting, similar to that seen in valuable alexandrite, commonly displaying blue or violet color in daylight, and red to red-violet under incandescent light. Star sapphires with the asterism effect are also available. These generally display a 6-Ray or very rarely even a 12-ray star.
SAPPHIRE SOURCES
Kashmir (India) - Sapphires from Kashmir are known for their beautiful velvety-blue, slightly milky color, similar to that of the cornflower. The mine area is in Zanskar, near the city of Soomjam in India. Gems said to originate from this source fetched extremely high prices – much higher than the prices given for Sri Lankan or even Myanmar sapphires of similar quality.
Myanmar - Myanmar is considered to be the world's second-most precious source for blue-colored sapphires. The two main sources are Mogok and Mong-Hsu. The color of the Myanmar sapphire is violetish Blue and it is commonly referred to as ‘Royal Blue’.
Thailand – The main sources of Thai sapphires are Kanchanaburi and Chantaburi. Thai sapphires are very dark blue (‘Navy Blue’) to almost black in color and can be classified into a number of color-types: Common Thai, Bankacha color and Kanjanburi color.
Sri Lanka - Corundum is found in many areas of Sri Lanka and in an astounding variety of colors, including the much-coveted padparadscha sapphires. The blue sapphire's color is generally weaker than the colors of the Myanmar variety. Since the early 1970s, sapphires from Sri Lanka have been heated according to a number of undisclosed methods, thereby improving their color. Today it is considered as the 3rd most prestigious source (after Kashmir and Myanmar).
Cambodia - Pailin, Cambodia, is a well-known source of fine blue sapphires. Cambodian sapphires tend to display rich saturated blue to violetish Blue color with an attractive lustre.
Madagascar - Madagascar is the world leader in sapphire production since 2007, after the discovery of enormous sapphire deposits in Ilakaka in 1998. Ilakaka and Andranandambo are the major areas for sapphires in Madagascar. Madagascar sapphires tend to present a highly-saturated, milky-apparent, violetish Blue color. Due to their resemblance, they are frequently confused with Kashmir and Sri-Lankan sapphires but their prices are much lower.
Tanzania - The Umba River and the Morogoro area in Tanzania are sources of fine sapphires in a wide range of colors. The Songea region is another source that produces sapphires with metallic Violet-Blue colors, with a noticeable greyish or greenish tint. The Songea gemstones are usually small and most of them have very strong pleochroism.
Australia - Australia is an important supplier of rough sapphires, mined mainly in New South Wales and Queensland and for years provided the majority of the cut merchandise in the market. Most of the small, cheap sapphires polished in Thailand are of Australian origin. Australian blue sapphires commonly display a slight greenish or greyish hue, a result of the heating process applied to most of the dark Australian merchandise to lighten the material and improve its clarity, and also possess distinct zoning characteristics.
USA - Montana sapphires display fine pastel Violet-Blue colors but also greyish Green, Green and Yellow to colorless hues. Pink to red gemstones are rarely found. The Montana gemstones are not homogeneous in color, are fairly included and generally have very strong zoning. The sizes of the rough extracted from the mine are small, rarely yielding gemstones above one carat.
Additional sources around the world include Vietnam, Laos, Kenya, Zimbabwe and Nigeria.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Variety: Sapphire
Species/Series: Corundum
Chemical Composition: Aluminum oxide (Al2O3)
Crystal System: Trigonal
Color: All colors, except red (blue, colorless, pink, orange, yellow, green, purple, black)
Hardness: 9
Refractive Index: 1.762 to 1.77 (+0.009/-0.005)
Specific Gravity: 4.00 (+0.10/-0.05)
Properties: RI 1.762-1.77 HARDNESS 9 SPECIFIC GRAVITY 4.0 SPECIES-CORUNDUM OPTIC CHARACTER-DR PHENOMENA-CHATOYANCY(VE
Reactions: Ultrasonic: usually safe Steamer: usually safe Heat: poor;may sometimes improve color, but may cause loss of color Chemicals: borax
Major Sources: Australia, Thailand, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, India
Grading Information: GEM, AAA, AA, A+, A, B
Specific Gravity: 3.99